SEA Ltd/Thales Alenia Space UK Ltd
Project Funded in the CEOI-ST 7th Call for EO Technologies.
Fast Track Project (up to 12 months duration)
SEA, in partnership with ESR, have developed a contactless power and data transfer device to TRL3 under ESA TRP funding, with an end objective to be available at TRL5 for the Metop Second Generation (M2G) programme. This has proven that 95% power transfer efficiency & high reliability data transfer at rates in excess of 5Mbps can be achieved and gives confidence that development to TRL5 can proceed with minimum schedule risk.
This project takes the existing prototype, designed for integration within a particular scan mechanism breadboard device and looks into adapting it for wider use as module on M2G and other missions by:
- Adjustment to maximise efficiency and adaptability for use on a range of instrument opportunities;
- Addition of new channels and interfaces into the data transfer system to ensure
- compatibility with a range of instrument data interface requirements;
- Adaptation to be accommodated as a module within the anticipated envelope available for Conical Scanners;
As such it offers a unique, high reliability solution to overcome the constraints.
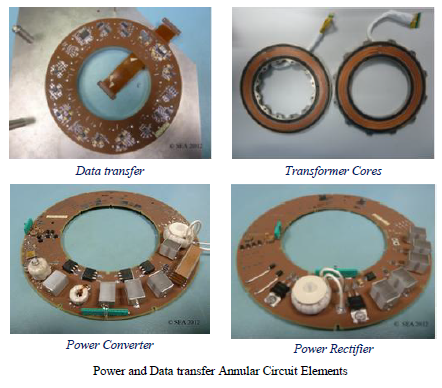
The 13 month CEOI-ST project has been successfully completed, achieving the following outcomes:
- Widened the range of input voltages supported and improve the power transfer efficiency at low voltages
- Added the ability to directly transfer thermistor and analogue signals
- Increased the speed of the serial data channel and converted to using SpaceWire
- Reduced the mass and modularised the housing to make the system a direct swap-out replacement for slip and roll rings
The project has enabled TAS-UK and ESR Technology to better position themselves to offer this new design as a direct replacement for slip and roll rings on space missions that have rotating elements. The team have also identified new opportunities and applications that this technology could be well suited to.
The next steps towards development for flight are:
- De-risking activities including prototyping of the new FPGA-based data transfer architecture and representative thermal, vibration and shock testing of the mounted transformer
- Development of an Engineering Qualification Model including a representative thermal vacuum accelerated life test to prove reliability (>100 million revolutions)
- Qualification to flight status
